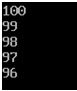
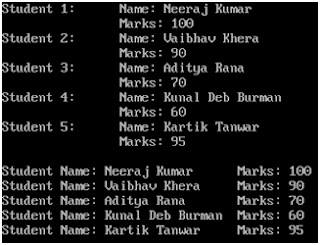
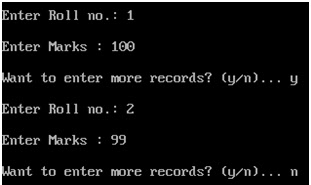
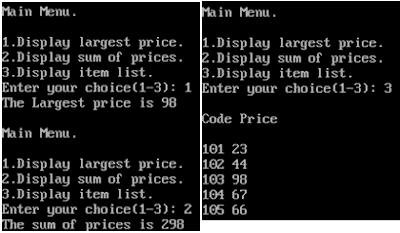
WAP that obtains the rotation factor and rotates the array as per it.
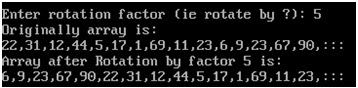
/* WAP that obtains the rotation factor and rotates the array as per it. */ #include<iostream.h> int main() { int Arr[15] = {22, 31, 12, 44, 5, 17, 1, 69, 11, 23, 6, 9, 23, 67, 90}; int r; cout<<"\nEnter rotation factor (ie rotate by ?): "; cin>>r; cout<<"Originally array is: "<<endl; for(int i=0;i<15;i++) cout<<Arr[i]<<","; cout<<":::"<<endl; //now rotate the array int temp[15]; for(i=14;i>=0;i--) { if((i+r) >=15) ...